
They have long, branched processes which occupy much of the interneuronal spaces in the neuropil. (a) Diagram (b) Immunohistochemical method for glial fibrillary acidic protein (HP)Īstrocytes are identified by immunohistochemical staining for a protein called glial fibrillary acidic protein ( GFAP) in micrograph (b) these are the most numerous glial cells in grey matter. Only some of the fibres are myelinated axons.

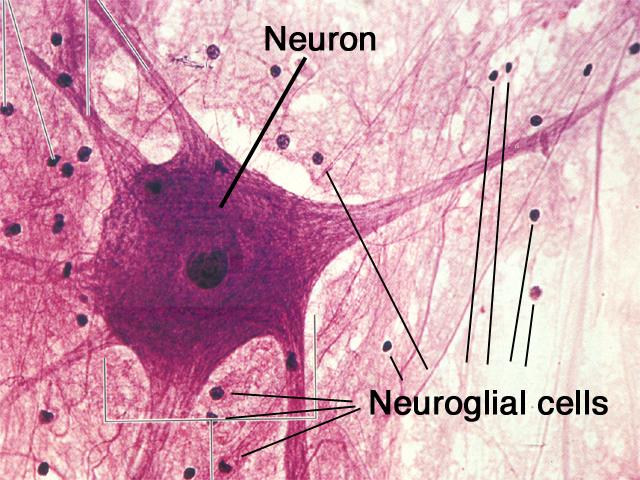
This is seen as a fibrillar eosinophilic material on H&E and is called neuropil Np. The nuclei of both neurones and neuroglia are surrounded by a dense network of branching cytoplasmic cell processes, axons and dendrites. Other glial cells in the image, marked A, are probably astrocytes. In grey matter, oligodendrocytes are not only scattered between the nerve cell bodies along with the astrocytes but also tend to be aggregated around the neurone cell bodies. In the mature CNS, as in this specimen, oligodendrocytes O have small round condensed nuclei their cytoplasm is unstained by routine methods, including H&E. Types of neuroglia are difficult to differentiate from each other with certainty by common staining methods. There is usually extensive basophilic granular cytoplasm, and parts of one or more processes may be visible, often due to processing artefact. While neurones vary greatly in different regions of the brain, they are usually recognisable by their large nuclei, prominent nucleoli and dispersed chromatin. In this chapter after description of the specialised supporting cells and tissues, including CSF production (choroid plexus), we will illustrate the microanatomy of some major structures in the CNS.Ĭommon staining methods permit neurones N to be readily distinguished from glial cells. While the basic organisation of grey and white matter remains consistent throughout the brain, in detail they form complex arrangements of the basic components to give a rich microscopic anatomy (histology) which is highly related to the macroscopic anatomy and function. The CNS also contains little extracellular material. Ependymal cells make up a specialised epithelium which lines the ventricles and spinal canalĬentral nervous tissue proper lacks collagenous supporting tissue which is confined to the immediate surrounds of penetrating blood vessels and to the meninges that invest the outer surface of the brain.Microglia are the CNS representatives of the monocyte-macrophage system and have defence and immunological functions.Astrocytes play an important role in repair of CNS tissue after damage They also form part of the blood-brain barrier. They provide mechanical support as well as mediating the exchange of metabolites between neurones and the vascular system. Astrocytes are highly branched cells that pack the interstices between the neurones, their processes and oligodendrocytes.Oligodendrocytes are the CNS equivalent of the Schwann cells of the peripheral nervous system and are responsible for the formation of myelin sheaths in the CNS.These are highly branched cells that occupy the spaces between neurones they have intimate functional relationships with the neurones, providing both mechanical and metabolic support.įour principal types of neuroglia are recognised: The lipid-rich myelin sheaths around the axons accounts for the white appearance of the white matter.Ĭentral nervous tissue consists of a vast number of neurones and their processes embedded in a mass of support cells, collectively known as neuroglia, which form almost half of the total mass of the CNS. Grey matter contains most of the neurone cell bodies and their dendritic processes while the white matter contains the axons. Macroscopically, all parts of the CNS are made up of grey matter and white matter. The CNS is invested with meninges and is suspended in fluid, the cerebrospinal fluid ( CSF) which is produced by specialised choroid plexus structures. The central nervous system (CNS) consists of the brain and spinal cord and is composed of neurones, neuronal processes, supporting cells of the CNS ( glial cells) and blood vessels.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
